Stamping
Pressing, Punching, Progressive stamping, Metal stamping
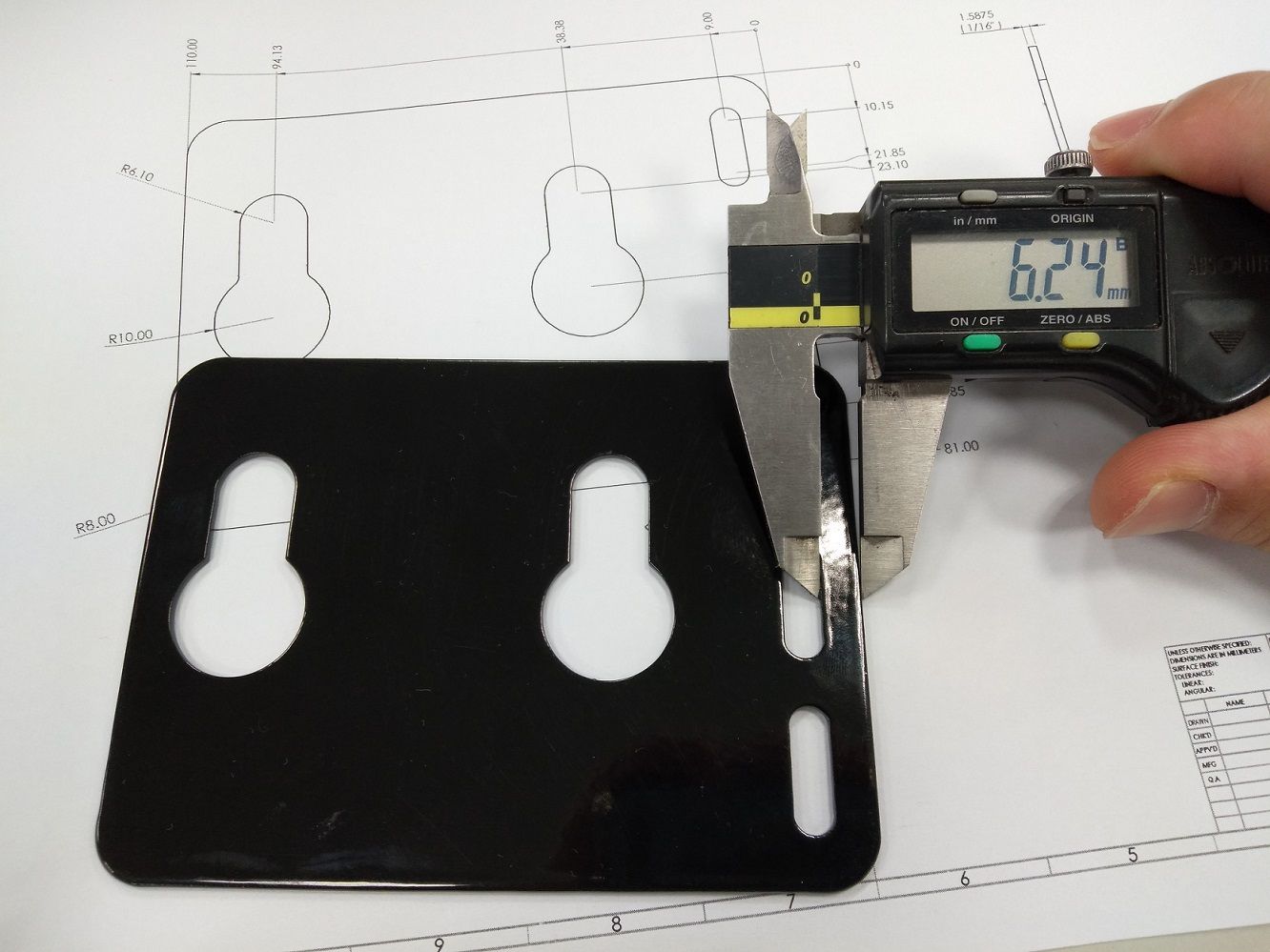
Stamping, also known as pressing, is a versatile metalworking process used to transform flat sheets or coils of metal into specific shapes and forms using a stamping press and dies.
It involves applying force to the metal workpiece to cut, shape, or form it into the desired configuration. The process typically includes various operations such as blanking(cutting out flat shapes), piercing(creating holes or perforations), bending(forming the metal into specific shapes or angles), and coining(adding features or shaping the metal surface), each using specialized dies and punches.
While stamping is able to produce intricate shapes and designs, its primary focus is on forming flat sheets or coils of metal into moderately complex shapes. This process offers some features owing to this formation, including:
Rapid Production Rates and Cost-Effectiveness for Mass Production: It enables efficient and high-speed production of parts once the dies and setups are prepared, making it suitable for mass production.
Consistent Quality and Repeatability: The process allows for consistent part quality and repeatability, ensuring that parts meet specified requirements and standards. This reliability is crucial in industries requiring consistent output.
Some common applications of Stamping include:
Car body panels, chassis components, kitchenware, building hardware, medical devices and manufacturing equipment.
